Drones Technology in Intelligent Construction
Drones are used for site surveying, progress monitoring, and inspections. They can capture aerial images and provide valuable data for project management. Drones, also known as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), have become an invaluable tool in the construction industry, enabling intelligent construction practices in various way.
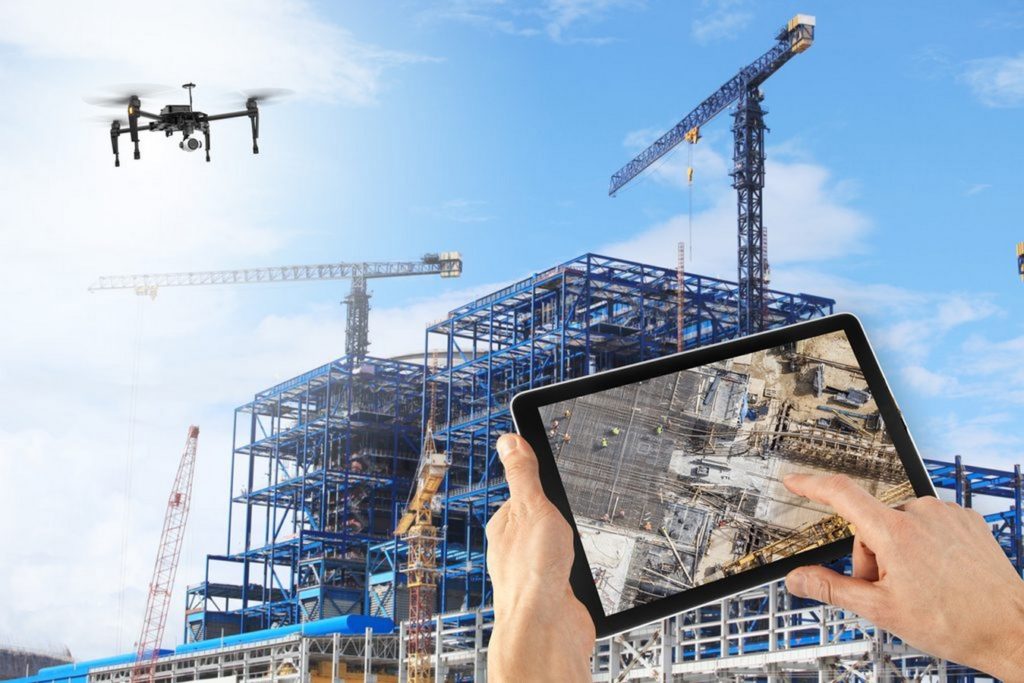
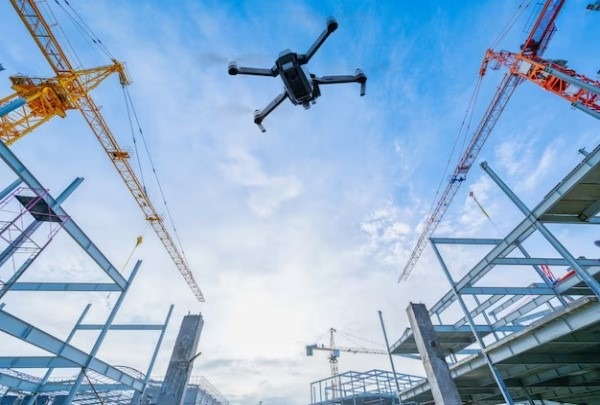


Aerial View of Drones
Applications of Drones in Intelligent Construction:
- Site Surveying and Mapping: Drones equipped with cameras and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors can quickly and accurately create topographic maps and 3D models of construction sites. This data is essential for site planning, design, and initial assessments.
- Progress Tracking: Drones can capture aerial images and videos of construction sites at regular intervals. These visuals are used to monitor progress, compare as-built conditions to plans, and identify potential delays or issues.
- Site Inspections and Safety: Drones can access hard-to-reach or hazardous areas, making it easier to inspect structures, roofs, and high scaffolding. They assist in identifying safety hazards and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
- Environmental Monitoring: Drones equipped with sensors can monitor air and water quality, noise levels, and environmental conditions on and around the construction site. This data helps maintain environmental compliance and minimize the project’s impact.
Benefits of Using Drones in Intelligent Construction:
- Efficiency: Drones can rapidly collect data and imagery, reducing the time and cost associated with manual surveys and inspections.
- Accuracy: They provide highly accurate and up-to-date data, minimizing errors in design and construction processes.
- Safety: Drones reduce the need for workers to access hazardous areas, enhancing overall construction site safety.
- Cost Savings: By improving project monitoring and reducing rework, drones contribute to cost savings and budget control.
- Environmental Compliance: Drones help construction companies adhere to environmental regulations and reduce environmental impact.
- Project Transparency: Aerial imagery and data provide stakeholders with a clear view of project progress and conditions.
Drones:
- Drones are equipped with cameras, sensors, and imaging technology, allowing them to capture high-resolution photos and videos of construction sites from various angles and altitudes.
- Some drones are equipped with LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors, which can create detailed 3D maps of the construction site.
- Before flight, operators create flight plans using specialized software. Flight plans specify the drone’s route, altitude, and waypoints.
- Drones are used for site surveying, where they capture topographic data and create accurate site maps, helping in initial site assessments, land surveying, and design planning.
- Drones capture images and videos of the construction site at regular intervals. These visuals are used for progress monitoring and documentation.
Types of Drones Used in Intelligent Construction:
- Fixed-Wing Drones: Fixed-wing drones are used for large-scale mapping and surveying tasks, as they can cover extensive areas efficiently. They are suitable for monitoring progress on large construction sites.
- Quadcopters: Quadcopters are versatile drones often used for general aerial photography, site inspections, and mapping tasks. They are highly maneuverable and easy to operate.
- VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) Drones: VTOL drones can take off and land vertically like a helicopter but can also fly like a fixed-wing aircraft. They are used for mapping and surveying large and challenging terrains.
- Hybrid drones: Hybrid drones in intelligent construction refer to unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that combine features of both fixed-wing and multirotor drones. These drones are designed to offer the advantages of both types of UAVs, making them versatile tools for various construction-related tasks.
- Surveying Drones: These drones are equipped with high-precision GPS and sensors to collect accurate topographic and geographic data, making them ideal for land surveying, site mapping, and earthwork calculations.


Case Study of Drones in Intelligent Construction:
- Problem: Site Surveying and Mapping
- Case Study: A construction company was facing delays and increased costs due to inaccurate site surveys and mapping, which led to design errors and rework.
- Solution: They implemented drones equipped with LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology to conduct highly accurate topographic surveys and 3D mapping of the construction site. This allowed for precise site modeling, reducing design errors and costly rework.
- Problem: Progress Monitoring
- Case Study: A construction project manager had difficulty tracking progress on a large site, leading to delays in decision-making and potential schedule overruns.
- Solution: Drones were deployed to capture aerial imagery and videos regularly. This data was then processed using AI algorithms to assess progress and identify any deviations from the schedule. Real-time progress tracking allowed for proactive decision-making and better project management.
- Problem: Materials Management
- Case Study: A construction company faced inefficiencies in materials management, leading to inventory shortages or overstocking.
- Solution: Drones were employed to monitor material stockpiles. They used photogrammetry and computer vision to measure stockpile volumes accurately. By tracking material levels in real-time, the company optimized material orders, reduced waste, and minimized inventory costs.